一. Multipartfile 方式文件上传
MultipartFi le 是 Spring 框架中的一个接口,它提供了一种方便的方式来处理文件上传。 它可以处理从表单中上传的文件,并提供了访问文件名称、大小、类型以及内容等信息的方法。 MultipartFile 接口还提供了一些实用的方法,如将文件保存到本地磁盘、将文件转换为字节数组等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestPart;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
@Controller
public class multipartfileController {
@Value("${file.upload.path}")
private String path;
@GetMapping("/")
public String uploadPage() {
return "upload";
}
@PostMapping("/upload")
@ResponseBody
public String create(@RequestPart MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
String filePath = path + fileName;
File dest = new File(filePath);
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), dest.toPath() );
return "Upload file success : " + dest.getAbsolutePath();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| 1. @Controller
作用:标记该类为 Spring MVC 中的控制器,负责处理 HTTP 请求。
场景:通常与@RequestMapping或其派生注解(如@GetMapping)配合使用,用于构建 Web 应用的控制器层。
1.1 @Override
显式声明重写:告诉编译器 “我正在重写父类 / 接口的方法”,如果实际没有正确重写(如方法签名不匹配),编译器会报错。
2. @Value("${file.upload.path}")
作用:从配置文件(如application.properties或application.yml)中读取属性值,并注入到变量中。
file.upload.path=/path/to/upload/
3. @GetMapping("/")
作用:处理 HTTP GET 请求,等价于@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "/")。
场景:常用于返回页面(如 HTML)或数据(如 JSON)。
示例:访问根路径/时,返回名为upload的视图(通常对应一个 HTML 模板)。
4. @PostMapping("/upload")
作用:处理 HTTP POST 请求,等价于@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, path = "/upload")。
场景:常用于提交表单数据或上传文件。
5. @ResponseBody
作用:将方法返回值直接作为 HTTP 响应体返回,而不是解析为视图名称。
场景:用于返回 JSON、XML 等数据格式。
示例:方法返回的字符串"Upload file success : ..."会直接作为响应内容返回给客户端
6. @RequestPart MultipartFile file
作用:绑定 HTTP 请求中的文件上传部分(通常来自表单的file字段)到MultipartFile对象。
依赖:需配置 Spring 的MultipartResolver(通常通过spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true自动配置)。
注意:
@RequestPart适用于处理multipart/form-data类型的请求。
@RequestParam也可处理文件上传,但@RequestPart更灵活,支持更多内容类型(如 JSON + 文件混合请求)。
总结:注解的核心作用
简化配置:替代传统的 XML 配置,使代码更简洁。
声明式编程:通过注解声明组件的角色(如控制器、服务)、请求处理方式(如 GET/POST)、依赖注入等。
AOP 支持:部分注解(如@Transactional)通过 AOP 实现额外功能(如事务管理)。
ps:
<form method="post" action="/upload" enctype="multipart/form-data">
action:表示表单的数据要发送到/upload路径中去
|
依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
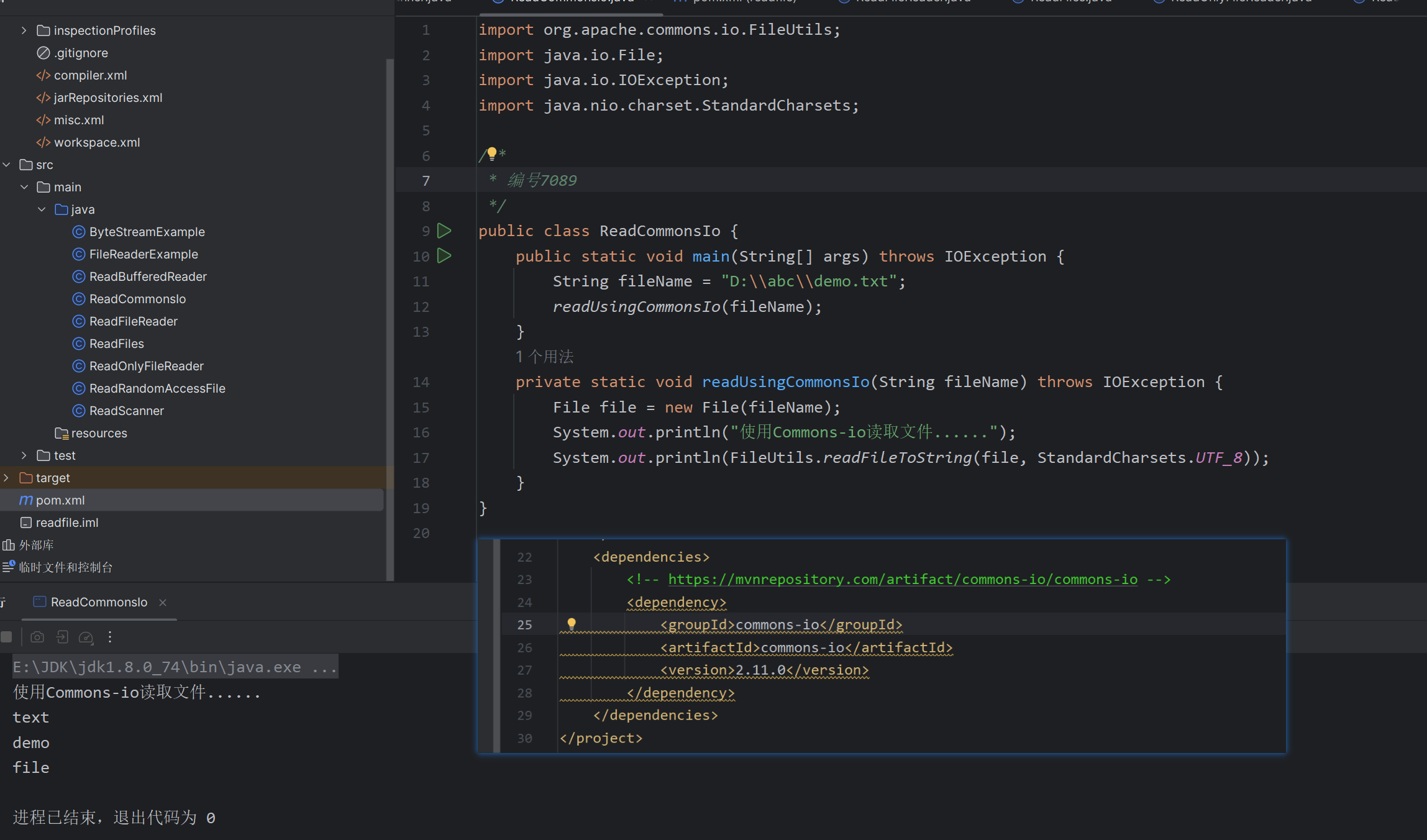
二、ServletFileUpload 方式文件上传
ServletFileUpload 方式文件上传依赖 commons-fileupload 组件。
对于 commons-fileupload 组件介绍:FileUpload依据规范RFC1867中”基于表单的 HTML 文件上载”对上传的文件数据进行解析,解析出来的每个项目对应一个 FileItem 对象。每个 FileItem 都有我们可能所需的属性:获取contentType,获取原本的文件名,获取文件大小,获取FiledName(如果是表单域上传),判断是否在内存中,判断是否属于表单域等。FileUpload使用FileItemFactory创建新的FileItem。该工厂可以控制每个项目的创建方式。目前提供的工厂实现可以将项目的数据存储临时存储在内存或磁盘上,具体取决于项目的大小(即数据字节,在指定的大小内时,存在内存中,超出范围,存在磁盘上)。
FileUpload 又依赖于 Commons IO。
| 方法 |
描述 |
| FileItemFactory |
表单项工厂接口 |
| ServletFileUpload |
文件上传类,用于解析上传的数据 |
| FileItem |
表单项类,表示每一个表单项 |
| public List parseRequest(HttpServletRequestrequest) |
解析上传的数据,返回包含 表单项的 List 集合 |
| String FileItem.getFieldName() |
获取表单项的 name 属性值 |
| String FileItem.getString() |
获取当前表单项的值 |
| String FileItem.getName() |
获取上传的文件名 |
| void FileItem.write(file) |
将上传的文件写到 参数 file 所指向存取的 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
| public class FileUploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
System.out.println("文件存放位置:"+realPath);
String tempPath = "C:\\Users\\powerful\\Desktop";
System.out.println("临时文件存放位置:"+tempPath);
File f = new File(realPath);
if(!f.exists()&&!f.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("目录或文件不存在! 创建目标目录。");
f.mkdir();
}
File f1 = new File(tempPath);
if(!f1.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("临时文件目录不存在! 创建临时文件目录");
f1.mkdir();
}
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
factory.setRepository(f1);
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
upload.setHeaderEncoding("UTF-8");
if(!ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(req)){
System.out.println("不是上传文件,终止");
return;
}
List<FileItem> items =upload.parseRequest(req);
for(FileItem item:items){
if(item.isFormField()){
String filedName = item.getFieldName();
String filedValue = item.getString("UTF-8");
System.out.println("普通字段:"+filedName+"=="+filedValue);
}else{
String fileName = item.getName();
if(fileName==null||"".equals(fileName.trim())){
continue;
}
fileName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("\\")+1);
String filePath = realPath+"\\"+fileName;
InputStream in = item.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
byte b[] = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len=in.read(b))!=-1){
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
out.close();
in.close();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
item.delete();
System.out.println("文件上传成功");
}
}
} catch (FileUploadException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("服务器繁忙,文件上传失败");
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
|
依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
</dependency>
|
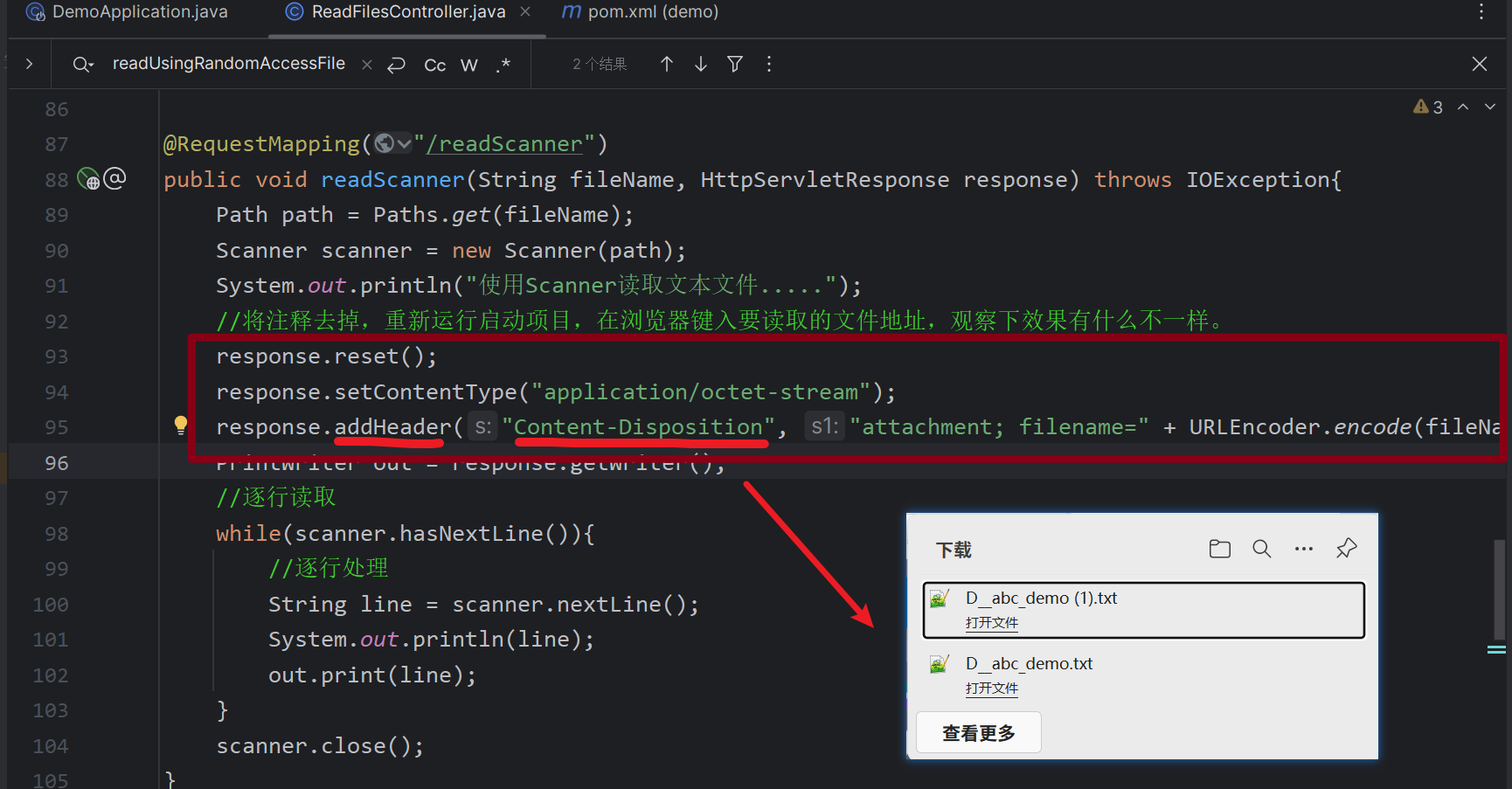
三. Java 文件操作之文件读取与下载
读取文件与下载文件在代码审计有何区别呢?
实际上在后端大多是通过读取文件方式获得目标文件内容,这个不难理解。最后将文件流内容传给浏览器,并在 header 头中添加浏览器解析方式和文件名,比如:文件下载到本地实现方法可以使用响应头 Content-disposition 来控制,也就是说下载这个动作是交给浏览器去操作的。
Content-Disposition 响应头:指示回复的内容该以何种形式展示,是以 内联 的形式(即网页或者页面的一部分),还是以 附件 的形式下载并保存到本地。
但从漏洞挖掘角度来看,我们使用下载或读取功能的目的是获得目标敏感文件中的数据。
实验:
方式一:使用 java.nio.file.Files 读取文本 (readAllBytes readAllLines)
使用 Files 类将文件的所有内容读入字节数组。 Files 类还有一个方法可以读取所有行到字符串列表。Files 类是在Java 7中引入的,如果想加载所有文件内容,使用这个类是比较适合的。只有在处理小文件并且需要加载所有文件内容到内存中时才应使用此方法。
在刚才创建的工程下的 src/main/java 目录下创建一个名为 ReadFiles 的Java Class。并键入以下代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.List;
public class ReadFiles {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:\\abc\\demo.txt";
readUsingFiles(fileName);
}
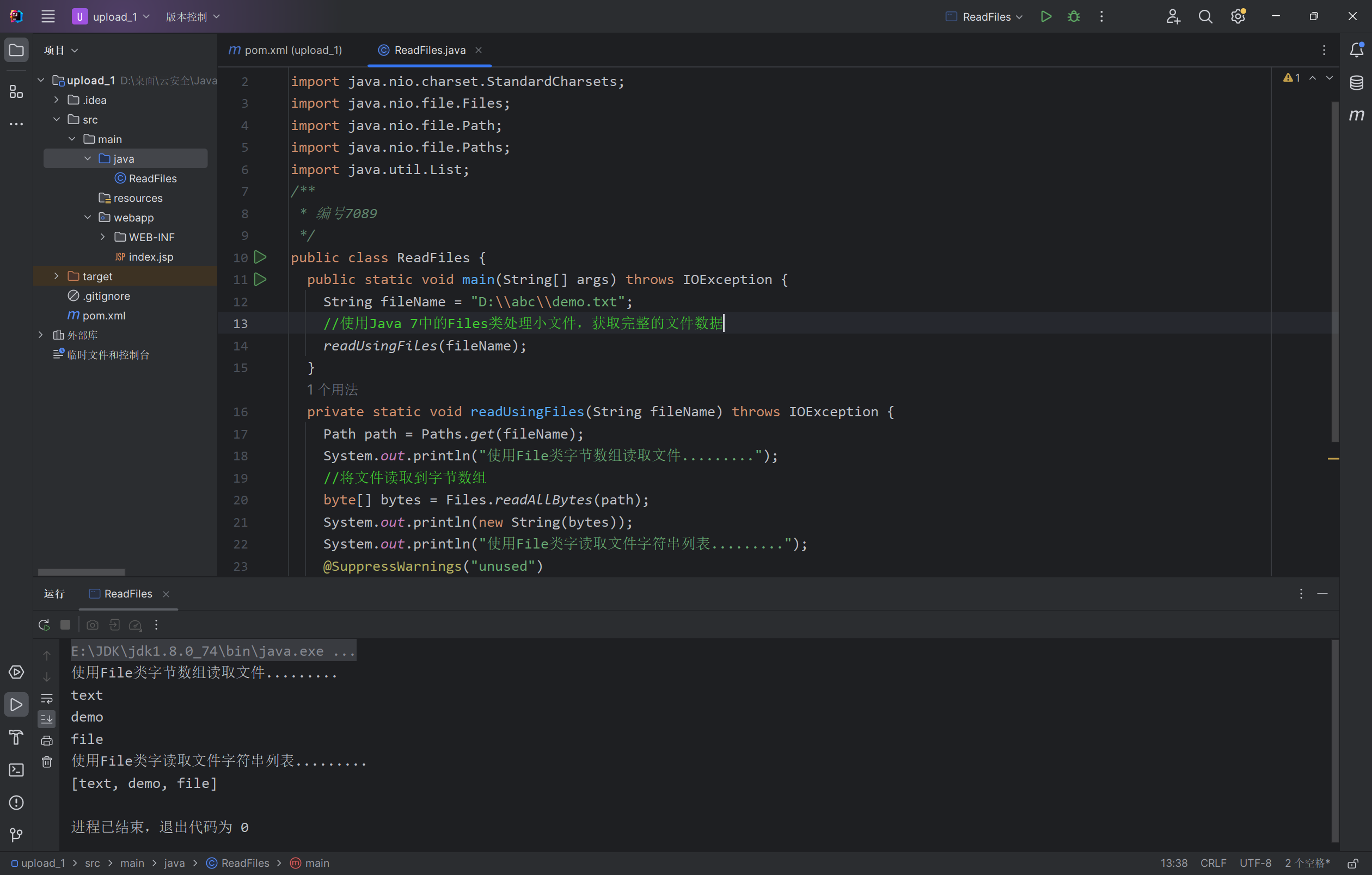
private static void readUsingFiles(String fileName) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
System.out.println("使用File类字节数组读取文件.........");
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
System.out.println("使用File类字读取文件字符串列表.........");
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
List<String> allLines = Files.readAllLines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(new String(allLines.toString()));
}
}
|
运行:
方法二:使用 java.io.FileReader 类读取文本
可以使用 FileReader 获取 BufferedReader ,然后逐行读取文件。 FileReader 不支持编码并使用系统默认编码,因此它不是一种java中读取文本文件的非常有效的方法。
在刚才创建的工程下的 src/main/java 目录下创建一个名为 ReadFileReader 的Java Class。并键入以下代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadFileReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:\\abc\\demo.txt";
readUsingFileReader(fileName);
}
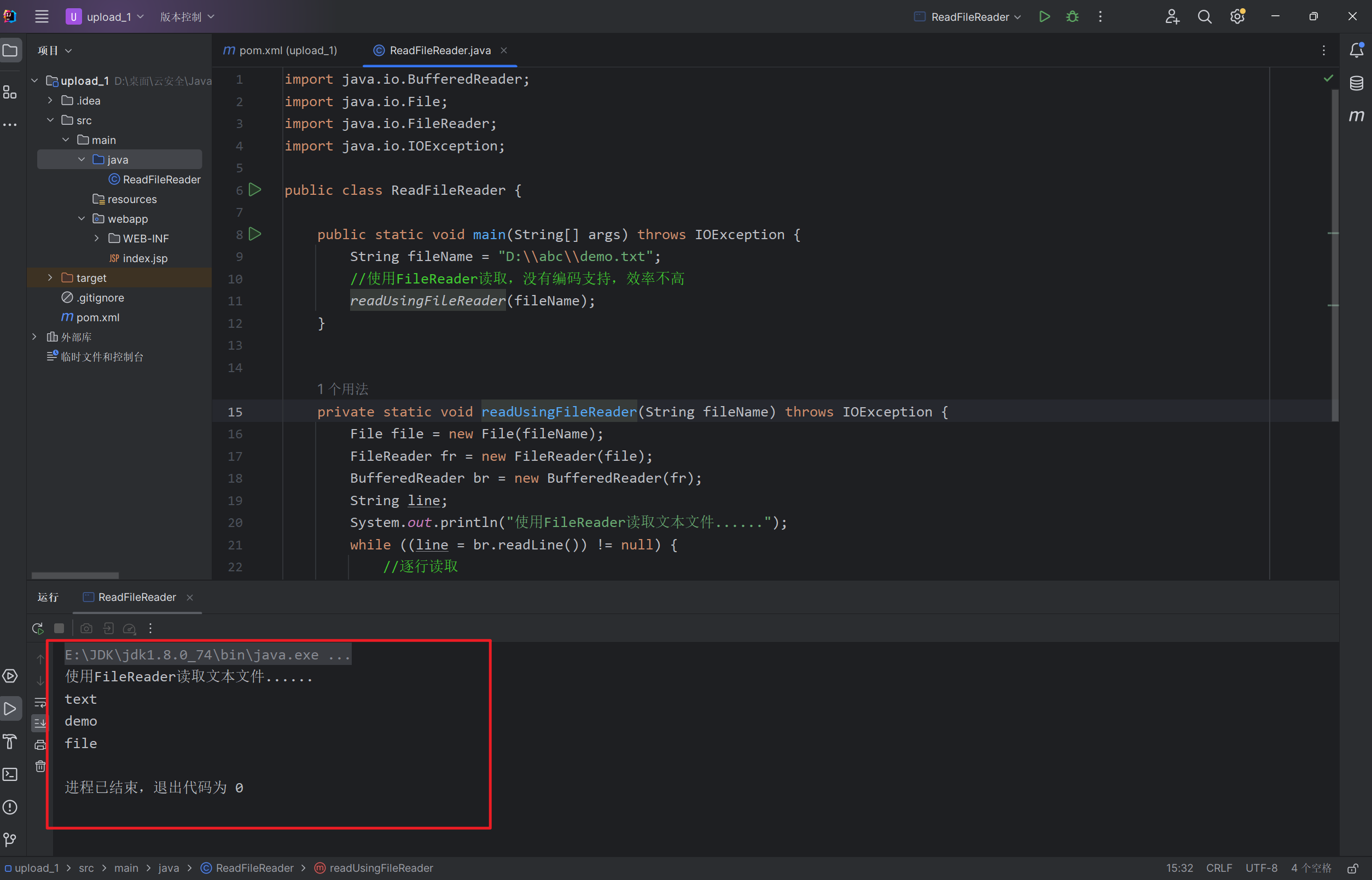
private static void readUsingFileReader(String fileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line;
System.out.println("使用FileReader读取文本文件......");
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
fr.close();
}
}
|
运行:
方法三:使用 java.io.BufferedReader 读取文本 (BufferedReader)
如果想逐行读取文件并对它们进行处理,那么 BufferedReader 是非常合适的。它适用于处理大文件,也支持编码。
BufferedReader 是同步的,因此可以安全地从多个线程完成对 BufferedReader 的读取操作。BufferedReader 的默认缓冲区大小为: 8KB
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class ReadBufferedReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:\\abc\\demo.txt";
readUsingBufferedReader(fileName, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
private static void readUsingBufferedReader(String fileName, Charset cs) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, cs);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
System.out.println("使用BufferedReader读取文本文件......");
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}
|
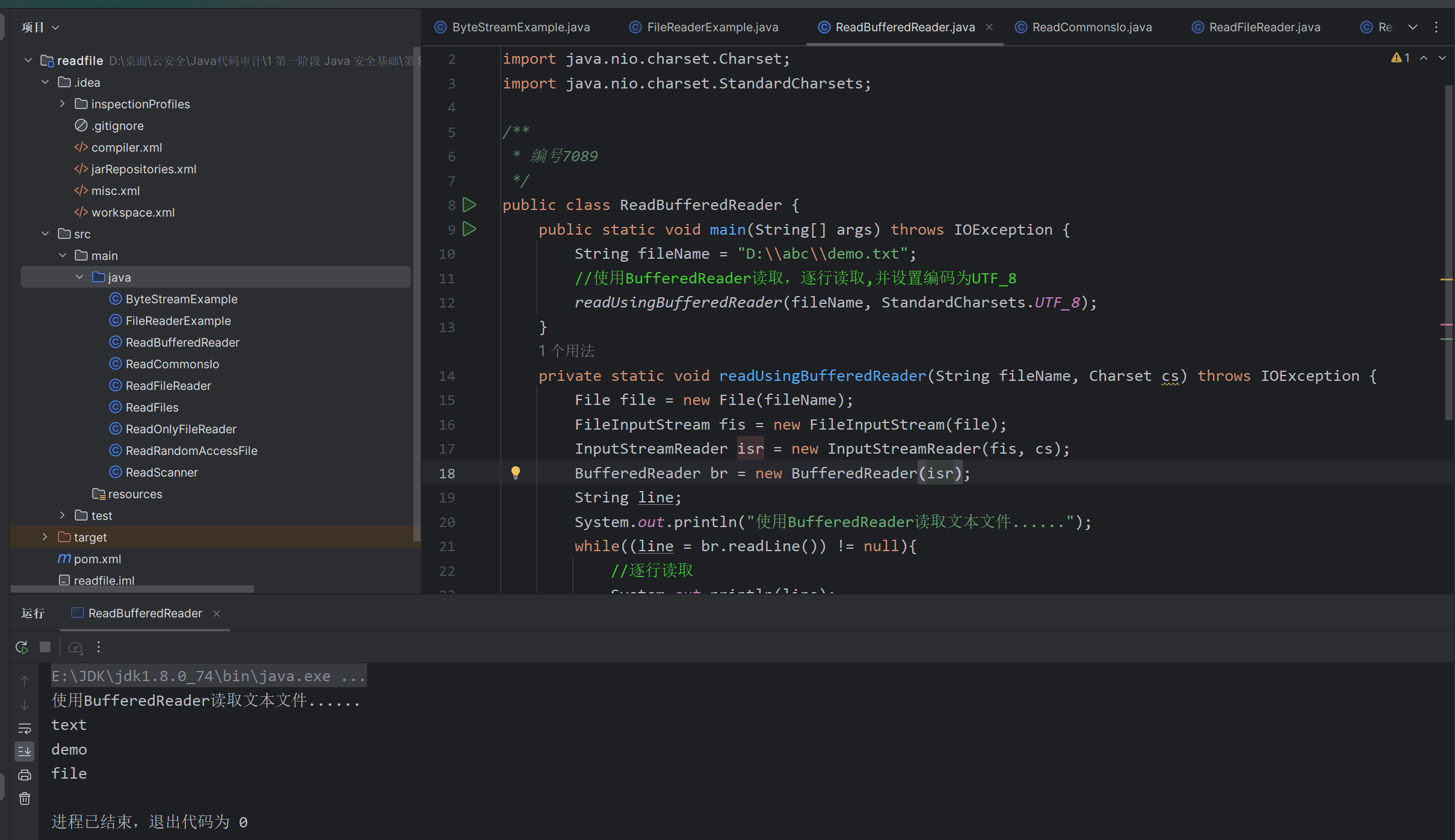
方法四:使用 Scanner 读取文本 (scanner.hasNextLine)
如果要逐行读取文件或基于某些java正则表达式读取文件,则可使用 Scanner 类。
Scanner 类使用分隔符模式将其输入分解为标记,分隔符模式默认匹配空格。然后可以使用各种下一种方法将得到的标记转换成不同类型的值。 Scanner 类不同步,因此不是线程安全的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadScanner {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:\\abc\\demo.txt";
readUsingScanner(fileName);
}
private static void readUsingScanner(String fileName) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(path);
System.out.println("使用Scanner读取文本文件.....");
while(scanner.hasNextLine()){
String line = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
scanner.close();
}
}
|
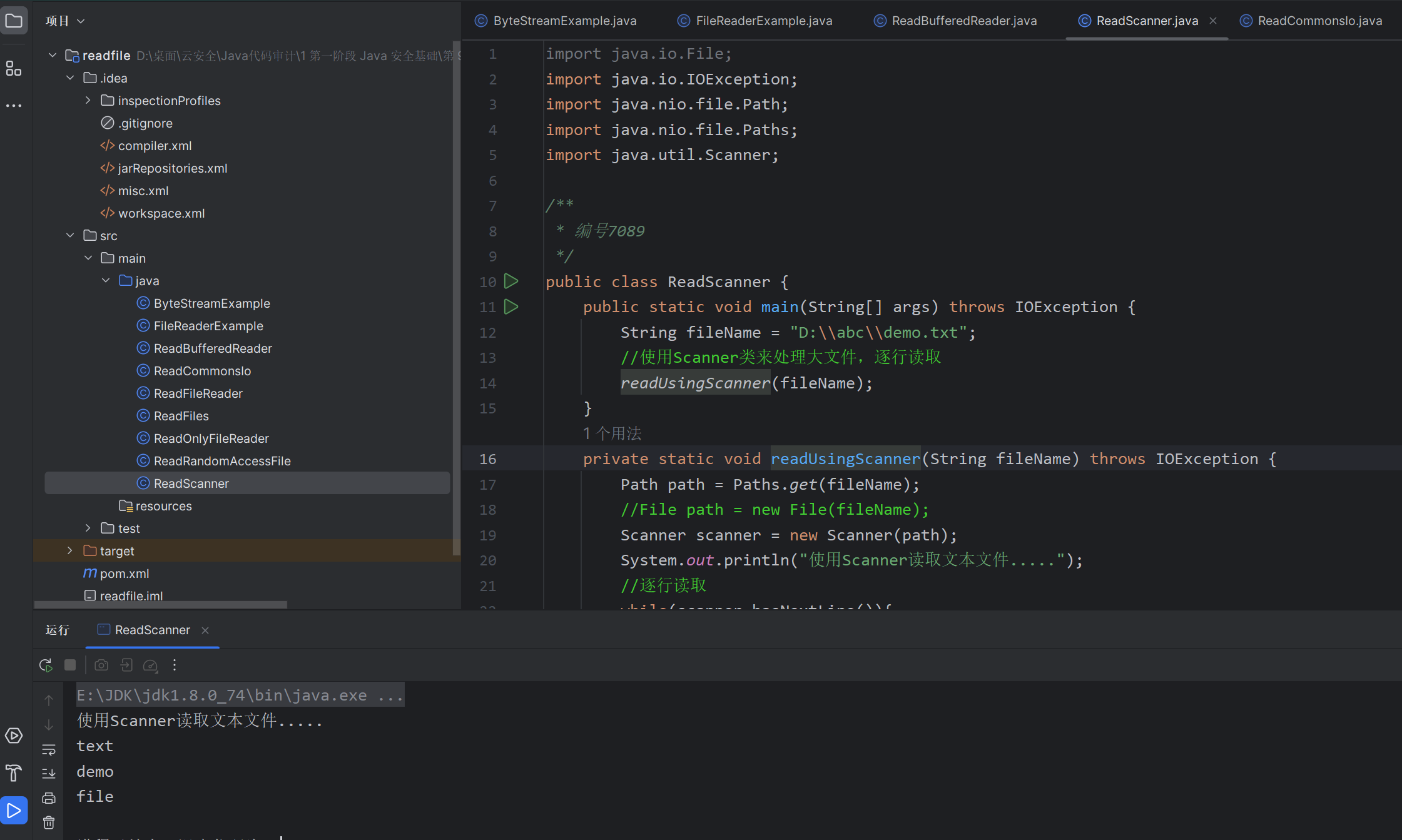
方法五:使用 RandomAccessFile 断点续传读取文本
随机流(RandomAccessFile)不属于IO流,支持对文件的读取和写入随机访问。首先把随机访问的文件对象看作存储在文件系统中的一个大型 byte 数组,然后通过指向该 byte 数组的光标或索引(即:文件指针 FilePointer)在该数组任意位置读取或写入任意数据。
断点续传是在下载或上传时,将下载或上传任务(一个文件或一个压缩包)划分为几个部分,每一个部分采用一个线程进行上传或下载,如果碰到网络故障,可以从已经上传或下载的部分开始继续上传或者下载未完成的部分,而没有必要从头开始上传或者下载。
断点续传实现原理:
- 下载断开的时候,记录文件断点的位置position;
- 继续下载的时候,通过RandomAccessFile找到之前的position位置开始下载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class ReadRandomAccessFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:\\abc\\demo.txt";
readUsingRandomAccessFile(fileName);
}
private static void readUsingRandomAccessFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r");
String str;
while ((str = file.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("使用RandomAccessFile来实现断点续传读取/下载文件......");
System.out.println(str);
}
file.close();
}
}
|
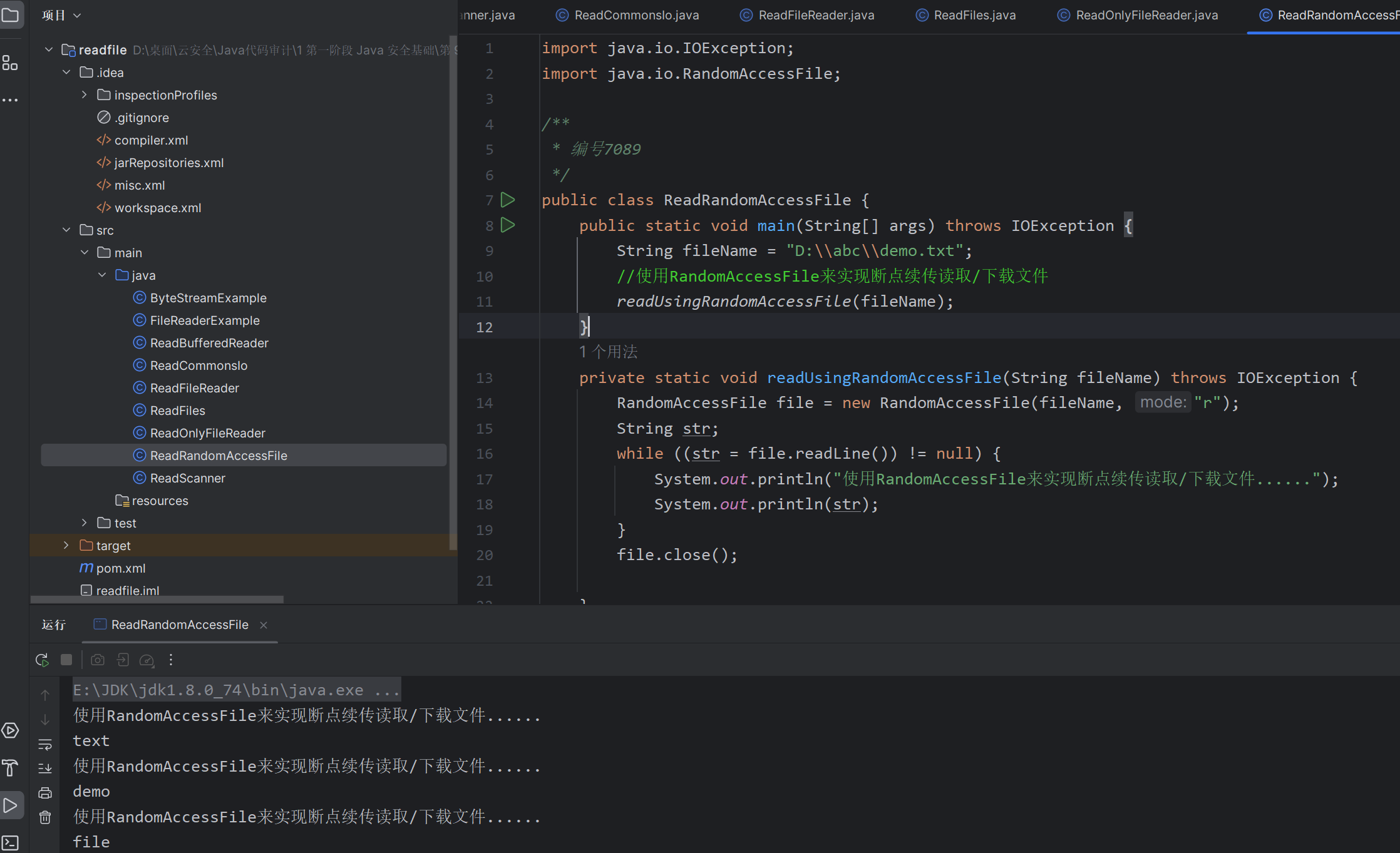
方式六:使用 commons-io 读取文本 (需要依赖)
文件操作: 提供了一系列用于文件复制、移动、删除和重命名的方法,还包括了获取文件大小、检查文件是否存在等常见操作。
流操作: 提供了用于处理输入和输出流的实用方法,如关闭流、复制流、转换流等。
文件过滤: 提供了一些实用的文件过滤器,可以根据文件名、文件大小、最后修改时间等条件对文件进行过滤。
目录操作: 提供了一些方便的方法来处理目录,如创建目录、列出目录内容等。
文件内容操作: 提供了一些用于读取、写入和比较文件内容的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class ReadCommonsIo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:\\abc\\demo.txt";
readUsingCommonsIo(fileName);
}
private static void readUsingCommonsIo(String fileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
System.out.println("使用Commons-io读取文件......");
System.out.println(FileUtils.readFileToString(file, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
方法七:使用 Files.readString 读取文本
Java 11添加了readString()方法来读取小文件String。官方介绍:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/nio/file/Files.html#readString(java.nio.file.Path,java.nio.charset.Charset)
1
| String content = Files.readString(path, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
|
四. 文件读取/下载 J avaWeb 工程
创建一个基于SpringBoot的读取文件的JavaWeb工程,这回我们从WEB角度调试上面几种方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
| package com.example.demo;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class ReadFilesController {
@RequestMapping("/readUsingFiles")
public String readUsingFiles(String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
System.out.println("使用File类读取文件.........");
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
List<String> allLines = Files.readAllLines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
response.reset();
response.setContentType("application/octet-stream");
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
return new String(bytes);
}
@RequestMapping("/readUsingFileReader")
public void readUsingFileReader(String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line;
System.out.println("使用FileReader读取文本文件......");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
out.print(line);
}
br.close();
fr.close();
}
@RequestMapping("/ReadBufferedReader")
public void readBufferedReader(String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException{
File file = new File(fileName);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
System.out.println("使用BufferedReader读取文本文件......");
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
out.print(line);
}
br.close();
}
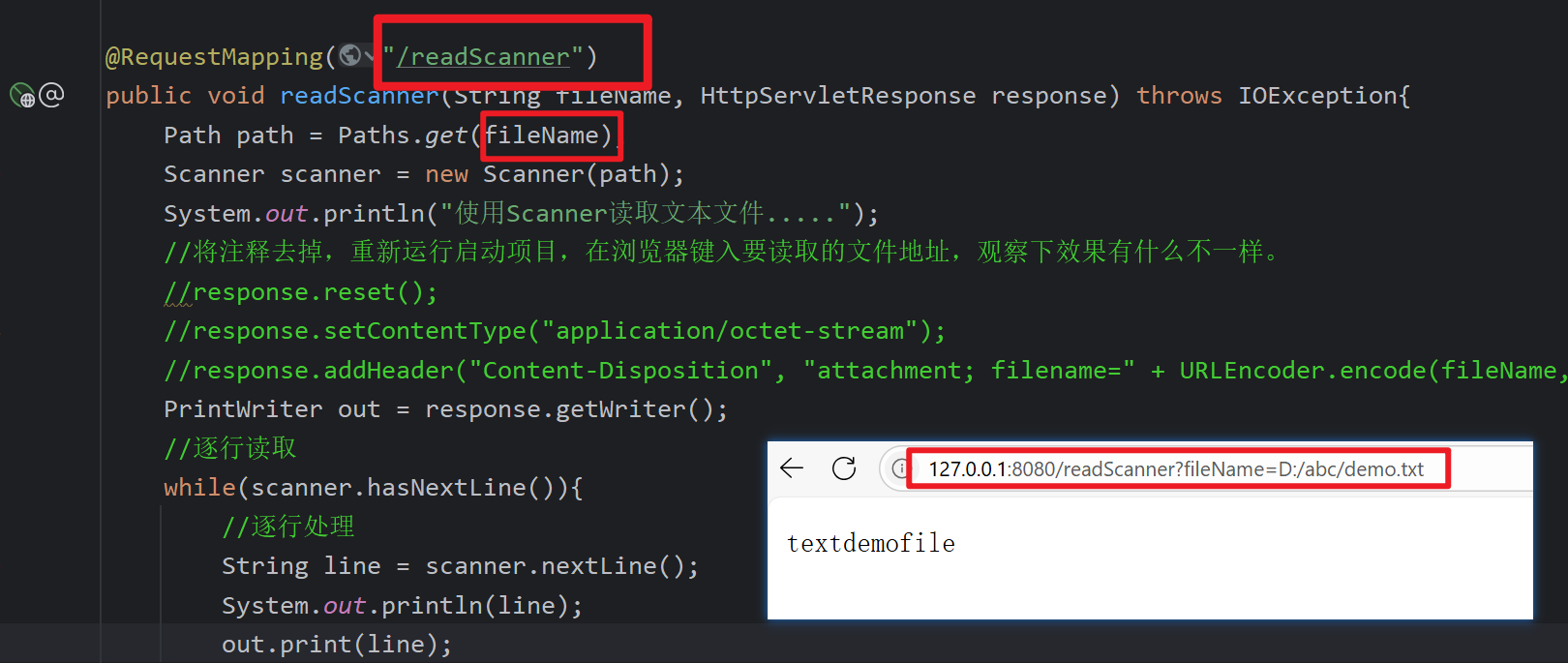
@RequestMapping("/readScanner")
public void readScanner(String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException{
Path path = Paths.get(fileName);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(path);
System.out.println("使用Scanner读取文本文件.....");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
while(scanner.hasNextLine()){
String line = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
out.print(line);
}
scanner.close();
}
@RequestMapping("/readUsingRandomAccessFile")
public void readUsingRandomAccessFile(String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException{
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r");
String str;
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
while ((str = file.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("使用RandomAccessFile来实现断点续传读取/下载文件......");
System.out.println(str);
out.print(str);
}
file.close();
}
@RequestMapping("/readUsingCommonsIo")
public String readUsingCommonsIo(String fileName,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException{
File file = new File(fileName);
response.reset();
response.setContentType("application/octet-stream");
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
System.out.println("使用Commons-io读取文件......");
System.out.println(FileUtils.readFileToString(file, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return FileUtils.readFileToString(file, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
}
|
依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.2</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
读取:
下载: